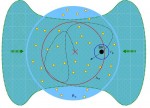
A small black hole gains mass. Dense cold gas (green) flows toward the centre of a stellar cluster (red cross in blue circle) with stars (yellow); the erratic path of the black hole through the gas (black line) is randomized by the surrounding stars. (photo from wis-wander.weizmann.ac.il)
At the ends of the universe, there are black holes with masses equaling billions of our sun. These giant bodies – quasars – feed on interstellar gas, swallowing large quantities of it non-stop. Thus, they reveal their existence: the light that is emitted by the gas as it is sucked in and crushed by the black hole’s gravity travels for eons across the universe until it reaches our telescopes. Looking at the edges of the universe is, therefore, looking into the past. These far-off, ancient quasars appear to us in their “baby photos” taken less than a billion years after the Big Bang: monstrous infants in a young universe.
Normally, a black hole forms when a massive star, weighing tens of solar masses, explodes after its nuclear fuel is spent. Without the nuclear furnace at its core pushing against gravity, the star collapses. Much of the material is flung outwards in a great supernova blast, while the rest falls inward, forming a black hole of only about 10 solar masses.
Since these ancient quasars were first discovered, scientists have wondered what process could lead a small black hole to gorge and fatten to such an extent, so soon after the Big Bang.
In fact, several processes tend to limit how fast a black hole can grow. For example, the gas normally does not fall directly into the black hole, but gets sidetracked into a slowly spiraling flow, trickling in drop by drop. When the gas is finally swallowed by the black hole, the light it emits pushes out against the gas. That light counterbalances gravity, and it slows the flow that feeds the black hole.
So how, indeed, did these ancient quasars grow? Prof. Tal Alexander, head of the particle physics and astrophysics department at the Weizmann Institute of Science, proposes a solution in a paper written together with Prof. Priyamvada Natarajan of Yale University, which appeared in a recent issue of Science.
Their model begins with the formation of a small black hole in the very early universe. At that time, cosmologists believe, gas streams were cold, dense and contained much larger amounts of material than the thin gas streams we see in today’s cosmos. The hungry, newborn black hole moved around, changing direction all the time, as it was knocked about by other baby stars in its vicinity. By quickly zigzagging, the black hole continually swept up more and more of the gas into its orbit, pulling the gas directly into it so fast, the gas could not settle into a slow, spiraling motion. The bigger the black hole got, the faster it ate; this growth rate, explained Alexander, rises faster than exponentially. After around 10 million years – a blink of an eye in cosmic time – the black hole would have filled out to around 10,000 solar masses. From then, the colossal growth rate would have slowed to a somewhat more leisurely pace, but the black hole’s future path would already be set – leading it to eventually weigh in at a billion solar masses or more.
Alexander’s research is supported by the European Research Council. Visit wis-wander.weizmann.ac.il for more Weizmann news.